A. NOTIFICATIONS
i) Notification No.1/2025-Central Tax dated 10th January, 2025
By the above notification, the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-1 for the month of December, 2024 and the quarter of October to December, 2024 is extended to 13th January, 2025, and 15th January, 2025 respectively.
ii) Notification No.2/2025-Central Tax dated 10th January, 2025
By the above notification, the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-3B for the month of December, 2024 and the quarter of October to December, 2024 is extended to 22nd January, 2025 and 24th January, 2025 respectively.
iii) Notification No.3/2025-Central Tax dated 10th January, 2025
By the above notification, the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-5 for the month of December, 2024 is extended till 15th January, 2025.
iv) Notification No.4/2025-Central Tax dated 10th January, 2025
By the above notification, the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-6 for the month of December, 2024 is extended till 15th January, 2025.
v) Notification No.5/2025-Central Tax dated 10th January, 2025
By the above notification, the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-7 for the month of December, 2024 is extended till 15th January, 2025.
vi) Notification No.6/2025-Central Tax dated 10th January, 2025
By the above notification, the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-8 for the month of December, 2024 is extended till 15th January, 2025.
NOTIFICATIONS (RATES)
CBIC has issued Notifications Central Tax (Rates)1 to 8 on 16th January, 2025. The effective date of notification and effect thereof may be summarized in brief, as follows:
CTR-1, effective from 16th January, 2025, notifies the rate of tax applicable on Fortified Rice Kernel. (Reduced from 18 per cent to 5 per cent). It also redefines the expression ‘pre-packaged and labelled’, for all commodities intended for retails sale.
CTR-2/2025, effective from 16th January, 2025, provides exemption from tax to “Gene Therapy”.
CRT-3/2025, effective from 16th January, 2025, provides for concessional rate of tax on food inputs of food preparations intended for free distribution to economically weaker section under a Government program.
CRT-4/2025, effective from 16th January, 2025, provides for increase in GST rate applicable on sale of old and used motor vehicles (from 12 per cent to 18 per cent).
(The taxable value is determined based on the margin of the supplier – same as earlier).
CRT-5/2025, is in respect of the rate of tax applicable on hotel accommodation services. (Effective from 1st April, 2025). The applicable rate of tax on such services, will now be decided based on the concept of “specified premises’” for a financial year, instead of earlier system of “declared tariff”.
CRT-6/2025, is in respect of certain services of insurance provided by the Motor Vehicle Accident Fund. (Effective from 1st April, 2025)
CRT-7/2025, effective from 16th January, 2025, provides for certain changes in applicability of provisions of RCM. Accordingly, now (1) “sponsorship services” provided by ‘any person other than a body corporate’ will attract RCM. (earlier the wordings were: ‘provided by any person’). (2) RCM, in respect of renting of Immovable Property (other than residential dwelling), provided by an un-registered person to a registered person, will not be applicable to those registered persons who have opted for ‘composition scheme’.
B. CIRCULARS
(i) Clarification on ITC availed by Electronic Commerce Operators – Circular no.240/34/2024-GST dated 31st December, 2024.
By the above circular, clarification is provided in respect of input tax credit availed by electronic commerce operators, where services specified under Section 9(5) of CGST Act are supplied through their platform.
(ii) Clarification on ITC as per section 16(2)(b) of CGST – Circular no.241/35/2024-GST dated 31st December, 2024.
By the above circular, clarification is provided on availability of input tax credit as per section 16(2)(b) of CGST Act in respect of goods, which have been delivered by the supplier at his place of business under Ex-Works Contract.
(iii) Clarification on place of supply of Online Services supplied to Unregistered recipient – Circular no.242/36/2024-GST dated 31st December, 2024.
By the above circular, clarification is provided in respect of place of supply of Online Services supplied by the suppliers of services to unregistered recipients.
(iv) Clarifications on issues related to GST treatment of voucher – Circular no.243/37/2024-GST dated 31st December, 2024.
By the above circular, clarification is provided on various issues pertaining to treatment of vouchers under GST.
C. ADVISORIES
i) Vide GSTN dated 18th December, 2024, guidance is provided for Entry of RR No./eT-RRs following the Integration of E-Way Bill with Freight Operation Information System of Indian Railways.
ii) Vide GSTIN dated 17th December, 2024, the information about updating to E-Way Bill and E-Invoice Systems is provided.
iii) Vide GSTIN dated 15th December, 2024, the information about Biometric based Aadhaar Authentication and Document Verification for GST Registration Applicants of Chhattisgarh, Goa and Mizoram is provided.
iv) Vide GSTIN dated 1st January, 2025, the information related to extension of E-way bills expired on 31st December, 2024, is provided.
v) Vide GSTIN dated 31st December, 2024, the information about Biometric based Aadhaar Authentication and Document Verification for GST Registration Applicants of Arunachal Pradesh is provided.
vi) Vide GSTIN dated 14th January, 2025, the information about Waiver scheme under Section 128A is provided.
vii) Vide GSTIN dated 14th January, 2025, the information about Generation date for Draft GSTR-2B for Dec, 2024 is provided.
viii) Vide GSTIN dated 8th January, 2025, the information about Biometric based Aadhaar Authentication and Document Verification for GST Registration Applicants of Rajasthan is provided.
ix) Vide GSTIN dated 7th January, 2025, the information about enabling of filing of Application for Rectification as per Notification no.22/2024-CT dt.8th October, 2024 is provided.
D. INSTRUCTIONS
The CBIC has issued instruction No.1/2025-GST dated 13th January, 2025 by which, instructions about guidelines for arrest and bail in relation to offences punishable under the CGST Act, 2017, are revised.
E. ADVANCE RULINGS
‘Tolerating an Act’ – Scope
Chamundeswari Electricity Supply Corporation Ltd. (AAR Order No. KAR/AAAR/02/2024 dated 6th November, 2024 (Kar)
The present appeal has been filed by the appellant, M/s. Chamundeswari Electricity Supply Corporation Limited, against the Advance Ruling order No. KAR/ADRG/09/2023 Dated: 27th February, 2023 – 2023-VIL-39-AAR.
The facts are that the appellant is a public sector company of Government of Karnataka, engaged in the distribution of electricity and supply of electric power in the districts of Mysore and others.
The Appellant is supplying electricity for housing, irrigation and also for all kinds of commercial and non-commercial purposes to the cliental comprising of individuals, farmers, organisations, hospitals, government organisations, commercial establishments, industries etc.
To meet the huge energy demand and universal supply obligation, it purchases power from central and state generating stations, private power generators which also include generators from non-conventional sources like wind, solar, mini hydel etc. The retail tariff is determined by the Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission, (KERC) as per the Electricity Act, 2003.
As per scheme, such Industries or companies can also buy power from private generators notwithstanding that they have entered into agreement with the appellant under “Open Access Consumers” (“OA Consumers” for short). To comply with the obligations created in agreement with its customer, the appellant enters into back-to-back Power Purchase Agreements (PPA) with private and state-owned energy generators to purchase power as back up for seamless supply of electricity assured to such customers.
The further relevant facts are as under:
The appellant collects an Additional Surcharge, the subject matter of this appeal, from Consumers when Consumers opt to buy electricity from third party private generators by invoking an open access clause.
The appellant has to pay third-party generators. Appellant recovers said amount from its customers under the heading of ‘Additional Surcharge’. The issue was about the liability of GST on the above collection.
In the above factual scenario, the appellant filed application for AR raising various different questions. The question (vii) was as under:
“vii. Whether Additional Surcharge collected from Open Access Consumer as per sub section (4) of Section 42 of the Electricity Act, 2003, clause 8.5.4 of the Tariff Policy 2016. Clause 5.8.3 of the National Electricity Policy and Clause 11(vii) of the KERC (Terms and Conditions for Open Access) Regulations, 2004, is taxable under the GST Acts?”
The ld. AAR answered the said question as under:
“vii. Additional Surcharge collected from Open Access Consumer as per subsection (4) of Section 42 of the Electricity Act, 2003, clause 8.5.4 of the Tariff Policy 2016, Clause 5.8.3 of the National Electricity Policy and clause 11(vii) of the KERC (Terms and Conditions for Open Access) Regulations, 2004, is taxable under GST Act.”
The main reason of ld. AAR to hold as above was that it interpreted the charges as for ‘tolerating an act’ and hence, a supply of service under GST Act.
The appellant was aggrieved by the above decision of ld. AAR and hence this appeal to ld. AAAR.
The ld. AAAR went through elaborate submission / grounds of appeal of the appellant. The main argument of appellant was that the appellant is collecting additional surcharge as per the Electricity Act; Tariff Policy; National Electricity Policy of Ministry of Power, Government of India and Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission (Terms and conditions for open Access) Regulation, 2004, KERC (Electricity Supply) Code, 2004 of Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission, Government of Karnataka from the open access customers, and therefore it forms part of tariff for the supply and distribution of electricity and cannot be taxable as separate service by way of ‘tolerating an act’.
The ld. AAAR also referred to Circular 178/10/2022-GST dated 3rd August, 2022 in which the concept of supply vis-à-vis ‘tolerating an act’ is explained.
The ld. AAAR observed that the collection of Additional Surcharge from OA consumers based on quantum of energy wheeled from the private generators is only to meet the fixed cost of the appellant arising out of this obligation to supply. Such collection mechanism is backed by an Act and policies of Central Government as well State Government. The ld. AAAR also observed that, the Appellant has entered into agreements with their customers, basically for supply of electricity and the money is collected by the Appellant in the form of Additional Surcharge, in situations where OA customer is not purchasing the entire requirement of electricity from them. The ld. AAAR also observed that there is no express or implied promise by the Appellant to agree to do or abstain from doing something in return for the money paid to them, rather they are ready to supply electricity as per the agreement. The ld. AAAR also observed that there is no independent arrangement entered into by the appellant for tolerating an act against which the consideration is collected as Additional Surcharge and, therefore, such amount do not constitute payment (or consideration) for tolerating an act.
Referring to section 15(2)(a), which provides that any taxes, duties, cesses, fees and charges levied separately under any law for the time being in force, other than GST, should be part of valuation of supply, the ld. AAAR held that Additional Surcharge levied under Electricity Act on their customers is part of taxable value and exempt along with electricity charges in terms of entry No. 104 of Notification No. 02/2017 CT(R) dated 28th June, 2017 applicable to goods and /or entry No.25 of the Notification No.12/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017 applicable to services and therefore not liable to tax.
The ld. AAAR thus allowed appeal in favour of appellant.
TAXABILITY OF VOUCHERS
Payline Technology Pvt. Ltd. (AAAR Order No. 04/AAAR/23/09/2024 dated 23rd September, 2024 (UP)
This appeal was filed by M/s. Payline Technology Pvt. Ltd. against the advance ruling no. UP ADRG-43/2024 dated 20.02.2024-2024-VIL-118-AAR, passed by the ld. UPAAR.
The facts are that the appellant is in the business of selling and purchasing Gift Cards, Vouchers, and pre-paid Vouchers closed or semi-dosed-ended vouchers (referred to as cards/voucher) against which goods or services can be purchased from specific brands on e-commerce platforms (such as Amazon, Flipkart, etc.). Appellant purchases cards from entities against advance payments at a discounted price. Thereafter, these vouchers are supplied to clients. The further fact is that once these vouchers are purchased by the appellant from the original issuers, the appellant becomes the
absolute owner of these vouchers, and both risk and reward lie with the appellant. It is noted that the appellant is neither the issuing person nor the user of these Vouchers.
The ld. AAR held that supply of Vouchers by the appellant are taxable @ 18% as per residual entry no.453 of the Third Schedule of Notification No.01/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dt.28th June, 2017.
Before the ld. AAAR, the appellant reiterated its ground that vouchers are very much in the nature of “money” and hence excluded from the definition of “Goods” as well as from “Services”, making the supply of these instruments non-taxable. The judgment in case of Premier Sales Promotion Ltd. relied upon.
It was further submitted that the goods/services are not identifiable at the time of issuance of said vouchers and hence, the time of supply of such vouchers shall fall at the time of their redemption which usually happens only after the cards are sold to the end consumers by the appellant. It was accordingly submitted that, there is no GST liability on cards sold by it.
The ld. AAAR referred to nature of vouchers considering the regulations of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in terms of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS)and the guidelines issued there under.
The ld. AAAR observed that the pre-paid payment instruments (PPI, in short) that can be issued in India can be classified under three categories. Looking at Guidelines given by RBI, the ld. AAAR observed that these conditions are mainly applicable to the issuers of the PPIs, and not to its traders, like appellant, as the Appellant is not the issuer of the voucher, but is the third party who buys and sells the vouchers.
The ld. AAR held that, the voucher in the hands of the appellant cannot be termed as “money”.
The ld. AAAR also analysed whether the vouchers are ‘goods’ or ‘services’.
For this purpose, reference made to definition of said terms in CGST Act. The ld. AAAR also verified whether it can be actionable claim. After discussion, the ld. AAAR observed that voucher by itself is a movable property and hence constitutes goods. It is further observed that since the voucher is in the possession of the claimant at the time of claim, it cannot be considered as actionable claim.
Further, referring to section 7(1) of CGST Act, the ld. AAAR held that it is taxable in hands of appellant.
The ld. AAAR deferred with the ld. AAR in respect of time of supply. In AR the ld. AAR has held that the sections 12(2) and 12(4) are not applicable to appellant. However, the ld. AAAR held that the section 12(4) of the CGST Act, 2017 is a specific provision for deciding the time of supply of the vouchers and is applicable to the appellant. Accordingly, the ld. AAAR held that time of supply of vouchers will be determined in terms of Section 12(4) of the CGST Act, 2017.
The ld. AAAR also held that in the present case, the appellant is engaged in trading of Vouchers/coupons and getting commission in the form of discount on such services, which are taxable.
Considering the above, the ld. AAAR held that trading in Vouchers/coupons, being a service, is the taxable event where the time of supply is when the Vouchers/coupons are traded or sold. It is also held that the value of service shall be the margin between the buying and selling price of the coupons.
Accordingly, the ld. AAAR modified AR holding that the supply of Gift voucher is a transaction of supply of goods and time of supply to be decided as per section 12(4) of CGST Act. It is further held that GST is applicable on the commission/discount earned in the trading of Vouchers/Coupons by the appellant and the time of supply will be the time when the Vouchers/ Coupons are traded or sold. It is further held that the value of service shall be the margin between the buying and selling price of the Vouchers/ Coupons.
[Note: The CBIC has issued Circular No.243/37/2024-GST, in which clarifications are given about taxability of voucher under GST.]
VALUATION – FREE OF COST SUPPLY
High Energy Batteries (India) Ltd. (Advance Ruling No. 28/ARA/2024 dated 6th December, 2024 (TN)
The applicant is engaged in manufacture of “Silver Oxide Zinc Torpedo Propulsion batteries” falling under Chapter sub heading No.850640 and secondary Silver Oxide Zinc Rechargeable Batteries falling under Chapter sub heading No. 8501780. It supplies the same to various Naval Defence formations (Indian navy) on payment of applicable GST.
The applicant submitted that the silver required for the manufacture of such batteries is supplied free of cost by the recipient, i.e. Naval formations by way of supplying their used batteries (non-serviceable). It was submitted that after extracting the silver from the used batteries supplied by Naval formations, the applicant manufactures the “Silver Zinc Batteries” as per the specification provided by the Naval formation and supplies the same to them. It was explained that while fixing the price for the batteries manufactured, the cost incurred by the applicant for extracting the silver from the old batteries is also included but the cost of the silver contained in the old batteries, supplied by the Naval formations free of cost in the form of old batteries, is not included in the taxable value for the purpose of payment of GST on the ground that the same is supplied free of cost by the Naval formations, who are the purchasers of the applicant.
It was also explained that the above mode of dealing is included in the contract signed between the applicant and their customer.
With above background, applicant raised following question before the ld. AAR.
“(1) Whether the value of the Silver supplied free of cost by the Naval Formations (in the form of old batteries) are to be included in the taxable value adopted by the applicant on the batteries manufactured by the applicant and supplied to the Naval Formations for the purpose of payment of GST or not.”
The applicant relied upon section 15(1) which provides for valuation as transaction value. The reference also made to definition of ‘consideration’ in section 2(31) of CGST Act. It was submitted that the transaction value agreed between the parties is only relevant for valuation purposes under GST and it is a matter of commercial arrangement between the supplier and recipient, as to what is in the scope of each of the parties. It was submitted that once it is clear that the supplier has to only supply final goods, then there is no question of adding the value of the free materials for determining the transaction value.
The ld. AAR observed that as per section 15(1) value of supply will be transaction value if,
a. the supplier and the recipient of the supply are not related parties.
b. the price is the sole consideration for the supply.
The ld. AAR observed that though the applicant and the recipient are not related persons, the consideration is not paid wholly in money. The ld. AAR, on perusal of the agreement, inferred that the contract is for the supply of Silver Oxide – Zinc Torpedo propulsion Battery Type A- 187M3- Complete with Hardware. It is further observed that the main input namely; Silver, is supplied free of cost against Bank Guarantee in the form of old and used batteries by the recipient, in addition to the consideration in money value for the supply of said Silver Oxide – Zinc Torpedo propulsion Battery. Therefore, the provision of Section 15(1) of the CGST Act, 2017 i.e. to adopt the transaction value as the value of supply of goods or services or both is not applicable for determining the value of supply in the applicant’s case, observed the ld. AAR. The ld. AAR observed that the consideration for the supply of Silver Oxide Zinc Torpedo propulsion Battery is paid in terms of money and Old and used Batteries.
The ld. AAR observed that old and used batteries are supplied by the naval formations i.e., by the Central Government Department to the applicant and for the said supply, unless otherwise exempted, the recipient of the said old used goods, that is the applicant, is liable for payment of Central tax and State Tax or as the case may be the Integrated Tax, as envisaged under Section 9(3) of the CGST Act or Section 5(3) of the IGST Act, read with corresponding Notifications issued, viz., Notification No.36/2017- Central Tax (Rate), dated 13/10/2017 and Notification No. 37/2017 Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 13th October, 2017, respectively.
The ld. AAR in this respect also referred to section 15(4) and Rule 27 and held that value of the taxable supply in case of applicant should be determined as per Rule 27(b) of CGST Rules,2017.
BLOCKED ITC U/S.17(5)(A) – NATURE OF EXCEPTION
A2Mac1 India Pvt. Ltd. (Advance Ruling No. 29/ARA/2024 dated 6th December, 2024 (TN)
The applicant is incorporated under the Indian Companies Act and is engaged in providing ‘Collaborative Automobile Benchmarking services’ by data management to the customers as a subscription package through an online platform where the detailed analysis of software concept of structure, process and global benchmarking data is made available.
From the database, the subscribers of the applicant get 360 degrees vehicle insights such as technology insights, cost insights, performance insights, market insights, sustainability insights, software insights, supply chain insights etc. and can use it for its own purpose. The applicant earns from subscription.
For vehicle benchmarking, the Applicant purchases brand new cars in the domestic market, disassembles them and adds research data to the corpus knowledge database for providing various insights to the customers. Motor vehicles bought by the Applicant are wholly and exclusively used for automotive research purpose carried out at the applicant’s factory. Hence, these vehicles are temporarily registered with RTO (Regional Transport Office).
The applicant also furnished a detailed process flow of the activities undertaken by it connected to vehicle dynamic benchmarking process with relevant images.
The cost of the vehicle bought and used for automotive benchmarking process is expensed out in the books by applicant. Further, at the end of specific/vehicle retention period, they are sold and the applicant is of the view that it is an activity of ‘supply’ in the course of its business and discharges applicable GST on such transactions.
The applicant was of view that ITC of tax paid on the purchase of new vehicles/cars is available to him as the applicant is providing taxable service using vehicles/cars for research purposes and the purchase of vehicles / cars are integral part of the business model. It was submitted that the cost of purchase of vehicles / cars are predominant to the business without which the main revenue stream of the Applicant i.e., supply of services via platform subscription would fail.
In above fact, the applicant sought to know whether the input tax credit on the purchase of vehicles/cars is claimable or not, in terms of Section 17(5)(a) of the CGST Act.
The applicant explained its eligibility to ITC on purchase of new motor cars explaining the scheme and intention of ITC with reference to various provisions like section 16(1) and 16(2) on CGST Act. The applicant also demonstrated its eligibility to get out of blocked credit in view of exception in section 17(5)(a)(A) on ground that for the Company’s business, the motor vehicles are indispensable tools for Research Study which in turn offered for subscription to the Customers.
The ld. AAR, for deciding the above issue, referred to section 17(5) which reads as under:
“(5) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1) of section 16 and sub-section (1) of section 18, input tax credit shall not be available in respect of the following, namely: –
2[(a) motor vehicles for transportation of persons having approved seating capacity of not more than thirteen persons (including the driver), except when they are used for making the following taxable supplies, namely: –
(A) further supply of such motor vehicles; or
(B) transportation of passengers; or
(C) imparting training on driving such motor vehicles;1
(aa) vessels and aircraft except when they are used-
…………”
The ld. AAR also referred to definition of ‘Motor Vehicle’ as provided in Section 2(76) of CGST which further refers to Motor Vehicles Act,1988 for merging of Motor Vehicles for purpose of GST Act.
The ld. AAR observed that Section 17(5) (a) blocks credit for ‘motor vehicle for transportation of persons’ and exceptions are available only to the three specified activities.
Referring to Circular No.231/25/2024-GST dt.10th September, 2024, the ld. AAR observed that the law is very clear and specific that except for the exceptions provided in sub-clauses (A), (B) and (C), the input tax credit on the purchase of vehicles, irrespective of any kind of outward supplies, shall not be eligible.
The ld. AAR observed that the applicant is seeking eligibility to ITC on the ground that the motor vehicles, used by them for making exhaustive analysis, are sold and the applicant is of the view that it is activity of ‘supply’ in the course or furtherance of business and discharges applicable GST on such transaction. However, the ld. AAR did not approve eligibility to ITC on above basis as it is not within Exception clauses (A), (B) and (C).
The ld. AAR, on perusal of the sample invoices relating to supply of motor vehicles after retention period, saw that the applicant is not classifying the product after use as ‘used or old motor vehicles’ but are supplying it as scrap of ‘Automobile part’ paying GST @ 18 per cent (CGST-9 per cent and SGST-9 per cent). The ld. AAR observed that the applicant is supplying the goods as ‘Scrap’ and therefore, the activity will not also fall within the scope of ‘further supply of such motor vehicles’. Accordingly, the ld. AAR held that the applicant cannot claim the exception and was not eligible to avail ITC on the motor vehicles purchased by them.
CLASSIFICATION – CHANGE OF TARIFF – PARTS OF SHIP
Imtiyaz Kaiym Barvatiya (Advance Ruling No. GUJ/GAAR/R/2024/19 (in application no.Advance Ruling/SGST&CGST/2023/AR/17) dated 3rd September, 2024 (Guj)
The facts are that the applicant imports various goods/spares, which are supplied on ships and it is the applicant’s contention that this equipment forms an essential part of the ship and makes the ship ‘sea worthy’. The goods are imported by the applicant on payment of IGST. The appellant has provided detailed list of equipments by way of Annexure. The name of equipments, description and utility as part of ship is explained in the said chart.
The applicant stated that they charge GST on parts/equipment supplied by them on the ship by classifying it under the same tariff head under which the goods are imported and discharges GST liability on supply based on rates applicable to such tariff entry. Instance is given that a “Standard Solas Model” is classified under tariff head “8479” captioned as “Ship Spares” and is taxed at the rate of 18 per cent.
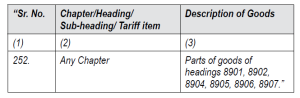
The applicant has further stated that the customer insists for GST at 5 per cent on the reasoning that these goods form part of ship and are covered at Sr. No. 252 of notification No. 1/2017-Central Tax (which covers parts of goods of headings 8901, 8902, 8904, 8905, 8906, 8907).
With above background the applicant has raised the following question for advance ruling viz;
“To decide as to whether the supply of goods [as listed in Annexure I-A of this ARA application is classifiable as “parts of goods of headings 8901, 8902, 8904, 8905, 8906, 8907” under entry 252 of Schedule I of GST Notification No. 01/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.6.2017 as amended and is liable to GST @ 5% (CGST-2.5% and SGST-2.5%) or IGST @ 5% or not.”
The applicant has relied upon the AAR ruling in the case of M/s. A. S. Moloobhoy Private Ltd. dated 18.7.2018 passed by the Maharashtra Authority for Advance Ruling-2018-VIL-232-AAR.
The ld. AAR reproduced entry 252 as under:
“Notification No. 1/2017-Central Tax dated 28.6.2017 Schedule I – 2.5%
The ld. AAR referred to the classification mechanism under GST including notes for classification under Customs Tariff.
The ld. AAR referred to one of the items for determination viz. “Standard Solas Model”, wherein the goods are classified under chapter heading 8479 as ‘ship spares’ and liability is discharged @ 18 per cent.
The ld. AAR noted that the applicant imports the goods and during the importation, the goods are classified by Customs under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975, and the applicant discharges the relevant customs duties including the IGST, which is applicable. It is also noted that the applicant willingly discharges the duties involved, which leads to the inference that he has agreed to the classification of the imported goods as done by the proper officer of Customs.
The ld. AAR observed that;
“18. On the aforementioned background, we find that the applicant is before us with an averment, that though the goods have been classified by Customs under various tariff items [as is mentioned in column 4 of the table above in respect of the bills of entry, the copies of which has been submitted vide email dated 29.7.2024] he now feels that consequent to the importation while undertaking further supply of the said goods, it should be classified under the heading 8901, 8902, 8904, 8905, 8906 & 8907 and thereby be eligible for benefit of Sr. No. 252 of notification No. 1/2017- CT (R) dated 28.6.2017. Availing the benefit of the said exemption notification, will make the supply leviable to GST @ 5%.”
In view of above the ld. AAR was to decide whether a change in classification is permissible.
The ld. AAR has opined in negative and held that change of classification is not permissible. The reasoning is based on the following factors.
“[a] the applicant without any protest agreed with the classification done by Customs and discharged the duties; and
[b] classification under GST is based on Customs Tariff Act, 1975, in terms of explanation (iii) and (iv) of notification No. 1/2017-CTR dated 28th June, 2017;
[c] that there is no change in the character of the goods supplied by the applicant to the one imported.”
The ld. AAR did not agree with the reliance of the applicant on the advance ruling dated 18th July, 2018 in the case of A S Moloobhoy Private Limited on the ground that it is applicable only to A S Moloobhoy Private Limited in terms of section 103 of the CGST Act, 2017.
In view of the above, the ld. AAR gave a ruling that the supply of goods given in application is classifiable under the same chapter, heading, sub-heading and tariff item under which the goods were imported and the rate of the supply of said goods would be in terms on the rates applicable to such respective tariff entry.














 It was also discussed how we can prioritize the different aspects of our life like Financial, Professional, Social, Personal, Physical, Spiritual and bring harmony and purpose in our life, while we grow as well as be happy all the time. The presenter taught how to overcome distractions in the way of accomplishments and retain the mindset to focus.
It was also discussed how we can prioritize the different aspects of our life like Financial, Professional, Social, Personal, Physical, Spiritual and bring harmony and purpose in our life, while we grow as well as be happy all the time. The presenter taught how to overcome distractions in the way of accomplishments and retain the mindset to focus.  This meeting was conceived by the Corporate and Allied Laws Committee of BCAS and was jointly organized with the BSE. Mr. Neeraj Kulshrestha (Chief of Business Operations – BSE) was the Guest of Honour, Mr. Ajay Thakur (Head – BSE SME) was the keynote speaker and Mr. Mahavir Lunawat, (Founder – Pantomath Group) was the speaker for the day. Mr. Kanu Chokshi (Chairman, Corporate & Allied Laws Committee) chaired the meeting. Mr. Raman Jokhakar (President, BCAS) welcomed the participants and highlighted the relevance of the topic in view of the proposed ‘Startup India’ and ‘Standup India’ initiatives, launched by the Government of India. Mr. Kanu Chokshi briefly introduced the speakers and the topic.
This meeting was conceived by the Corporate and Allied Laws Committee of BCAS and was jointly organized with the BSE. Mr. Neeraj Kulshrestha (Chief of Business Operations – BSE) was the Guest of Honour, Mr. Ajay Thakur (Head – BSE SME) was the keynote speaker and Mr. Mahavir Lunawat, (Founder – Pantomath Group) was the speaker for the day. Mr. Kanu Chokshi (Chairman, Corporate & Allied Laws Committee) chaired the meeting. Mr. Raman Jokhakar (President, BCAS) welcomed the participants and highlighted the relevance of the topic in view of the proposed ‘Startup India’ and ‘Standup India’ initiatives, launched by the Government of India. Mr. Kanu Chokshi briefly introduced the speakers and the topic. Moving to the product zone, the team saw samples of each product processed out of the refinery, namely Propylene, Naptha, Gassoline, Jet/Aviation Turbine Fuel, Sulphur, Petcock etc. Participants were fortunate to visit control room. The entire refinery is controlled from this area. The control room has earmarked the area for each unit – Fluid catalytic cracking unit (FCCU), clean fuel plant (CFP), Hydrogen manufacturing unit (HMU), Reliance tank farm (RTF ) and so on.
Moving to the product zone, the team saw samples of each product processed out of the refinery, namely Propylene, Naptha, Gassoline, Jet/Aviation Turbine Fuel, Sulphur, Petcock etc. Participants were fortunate to visit control room. The entire refinery is controlled from this area. The control room has earmarked the area for each unit – Fluid catalytic cracking unit (FCCU), clean fuel plant (CFP), Hydrogen manufacturing unit (HMU), Reliance tank farm (RTF ) and so on.